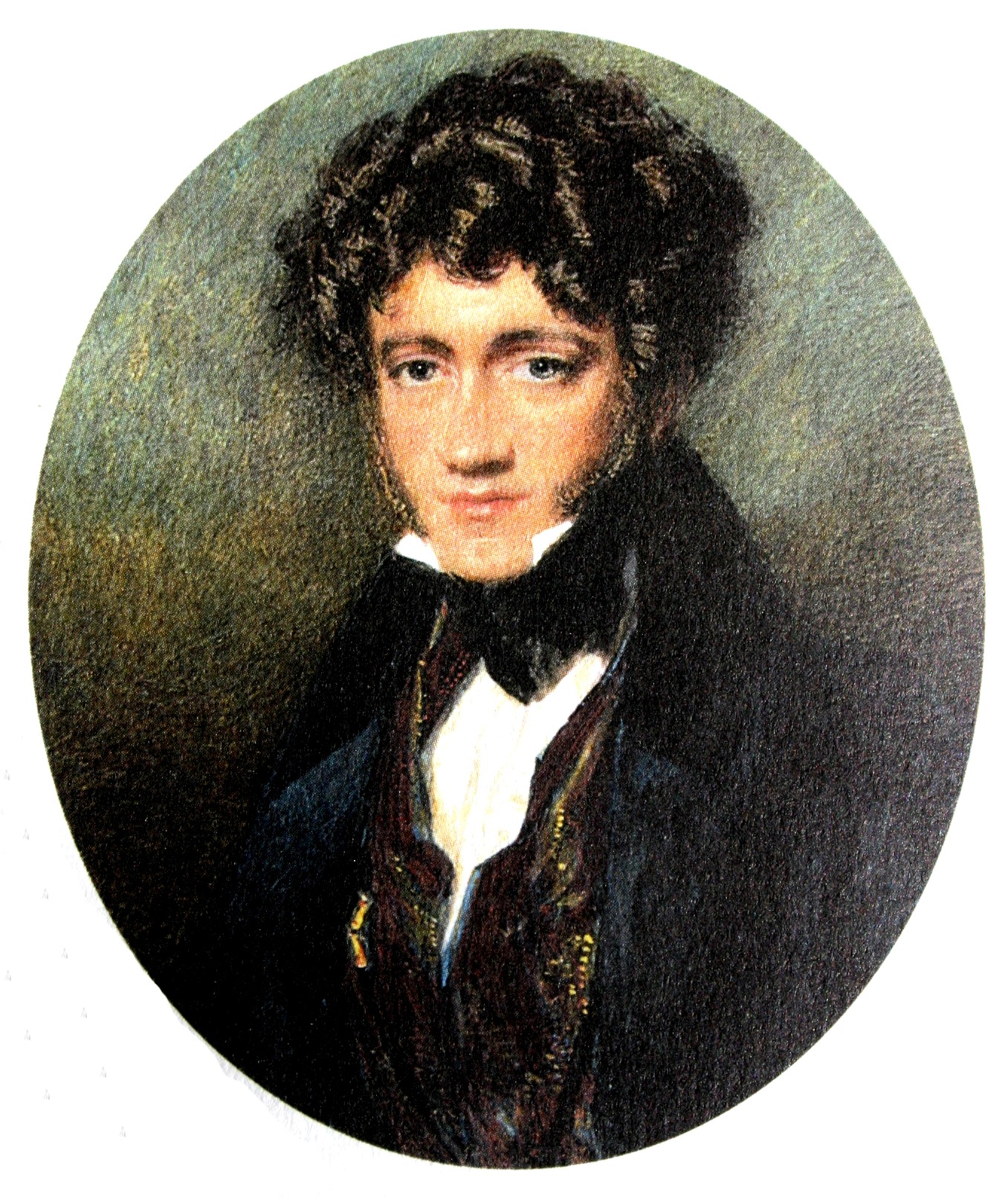
Nadar
Gaspar -Felix Tournachon (also known as Nadar) was born on the 6th April 1820 to a liberal publisher. He had only one brother, five years younger named Adrien.
Nadar began his studies in medical school while working for newspapers. Later he gave up medicine to focus on journalism.
He first became famous for the sarcastic caricatures of well-known political figures, which he used to sell to newspapers. It was at that time that he was nicknamed 'tourne a' dard' - "the one who stings or twist the dart", which was later shortened for Nadar. (Imaging Resource,1998-2013)
Nadar introduced his brother Adrien to photography during the same time that F. Scott Archer invented the collodion -on -glass process, while he took some lessons himself. He became more interested in photography since it was a medium that could help him in his drawings.
In 1853, Nadar convinced his brother to run a photo studio for him, however it was not going very well due to Adrien 's disorganization. He opened his own five years later.His clients used to be celebrities such as writers, artists and musicians who most of them happened to be his friends.
In 1858, Nadar produced his first aerial photograph from a hot-air balloon, which image no longer survive.
The oldest existing aerial photograph of Boston which was taken by James Wallace Black on the 13th October 1860.
Due to great demand , Nadar moved to larger premises at Boulevard des Capucines in 1860.
Innovative Nadar was also the first to photograph the sewers and the catacombs of Paris with artificial light.
His achievement with his balloon " le Geant" in 1863, made Nadar an international figure.
In 1886, he made his first photo-interview of history with the with the centenarian chemist Michell-Eugene Chevreul.
In April 1874, Nadar lent his studio for the Exhibition of the Impressionist painters.
He wrote his autobiography - "Nadar- when I was a Photographer" at the age of 80.
Nadar died 9 years later on the 20th March 1910 and was buried in the Cemetery Pere-Lachaise in Paris.
References :
The Museum of Modern Art,2013.The Collection.[online] Available at : <http://www.moma.org/collection/artist.php?artist_id=4196 >[Accessed 25 October 2013].
Podolski Consulting,2001-2011.History of Aerial Photography.[online] Available at : < http://www.papainternational.org/history.asp > [Accessed 25 October 2013].
Photographic Art & Science Foundation,2013. Nadar (Gaspar Felix Tournachon).[online] Available at : <
http://www.iphf.org/hall-of-fame/nadar-gaspard-felix-tournachon/> [Accessed 25 October 2013].
Masters of Photography,(n.d).Text from a World History of Photography.[online] Available at : < http://www.masters-of-photography.com/N/nadar/nadar_articles2.html > [Accessed 25 October 2013].
The Imaging Resource,1998-2013.The incomparable Nadar- Master photographer, political cartoonist & balloonist of the 19th Century Paris. [online] Available at : < http://www.imaging-resource.com/news/2013/03/22/the-incomparable-nadar-master-photographer-cartoonist-balloonist-of-paris > [ Accessed 25 October 2013].
A.D. Coleman/PCCA,2003-2005.Nadar (Gaspar Felix Tournachon) 1820-1910. [online] Available at : < http://www.photocriticism.com/members/archiveauthors/nadarpcca.html > [ Accessed 26 October 2013].
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000-2013.Nadar(1820-1910). [online] Available at : < http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/nadr/hd_nadr.htm > [ Accessed 26 October 2013].
Art Directory GMbh, (n.d). Nadar. [online] Available at : < http://www.art-directory.info/photography/nadar-1820/index.shtml > [Accessed 26 October 2013].
Sir John Frederick Herschel
Sir John F. Herschel who was a famous British astronomer, mathematician, biologist and photographic chemist was born on the 7th March 1792, in Slough, Berkshire England to the astronomer Sir William Herschel and his wife Mary Pitt.
At the age of 8 he was sent to Eton College, but removed shortly after from his mother after he was bullied by other boys. He continued his studies by a private tutor until he attended St John 's College from where he graduated as Senior Wrangler.
In 1814 he decided to start a career in law, but after less than 2 years he moved back to Cambridge to teach mathematics.
In 1816, he moved back home to continue on his father 's steps in astronomical research.
The Royal Astronomical Society was established in 1820 and he was one of the founders.
He married his wife Margaret Brodie Stewart in 1829 and had 12 children.
In 1833 he left, for five years, to South Africa with his wife to catalogue nebulae and double stars some of which were were discovered by his father himself.
It was early in 1819 that he discovered the hyposulfite of soda, as a solvent for silver salts. However it was only twenty years later that he recommended it as a photographic fixing agent.
In 1842, while 'trying to find a a way of copying his notes' Herschel invented the Cyanotype also known as the blue print, due to white image on a blue background. (Alternative Photography).
He was the first one who introduced the terms "positive", "negative" and "snap-shot" to describe photographic images.
In 1850 he was appointed as Master of the Mint. The pressure and stress at work caused his health to decline and he even suffered from a nervous breakdown.
He resigned in 1856 and continued his work in astronomy.
Herschel died in May 1871 at Collingwood and was buried at Westminister Abbey.
References :
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013.Sir John Herschel,1st Baronet. [online] Available at :< http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/263809/Sir-John-Herschel-1st-Baronet > [Accessed 23 October 2013].
Alternative Photography,2000.Cyanotype history- John Herschel 's invention. [online] Available at : < http://www.alternativephotography.com/wp/history/cyanotype-history-john-herschels-invention > [Accessed 23 October 2013].
Cultural Compass,(n.d).From blue skies to blue print: Astronomer John Herschel 's invention of the Cyanotype. [online] Available at : <http://blogs.utexas.edu/culturalcompass/tag/sir-john-herschel/ > [Accessed 23 October 2013].
Wikipedia,2013. John Herschel.[online] Available at : <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Herschel >[Accessed 23 October 2013].
JOC/EFR,1999.John Frederick William Herschel. [online] Available at : <http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/Biographies/Herschel.html > [Accessed 23 October].
Kraszna-Krausz,A.,1978.The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography,Desk Edition, London:Focal Press. [Accessed 23 October 2013].
Boulevard du Temple - by Louis Jacques-Mande Daguerre
This photo named the Boulevard du Temple was taken by the inventor of photography Louis Jacques-Mandé Daguerre himself. It was taken early in the morning between April and May 1838.
This picture is very famous because of the two small figures of a man having his boots polished by a shoe shine boy in the corner of the street, as these were the first human beings to be photographed. There are different opinions if they were staged purposely for the photo or if they were unaware of being photographed.
The street in Paris at that particular time (eight in the morning) which is also indicated by the shadows of the trees would have been quite busy with passers-by and traffic, however due to the long exposure of about 10 to 12 minutes they could not be recorded.
The sharp image which is reversed is a documentary one of an urban part in Paris, although not in full details due to long exposure as explained above.
It is composed very well as the street is leading the viewer to the centre of the photo with a lot of depth of field. The linear contours of the tree trunks and the poles next to each other help to make a pleasing composition. The two human beings in the picture are also placed approximately in the rule of thirds.
These inventors and scientists at that time although they were still experimenting, had an eye to detail and composition and were also very artistic.
References:
Scott,Alistair,(n.d).Great Photographs No.1.[online] Available at : <http://www.alistairscott.com/daguerre/>[Accessed 29 October 2013].
Joseph Nicephore Niepce
Joseph Nicephore Niepce was born on the 7th March 1765 in Chalon-Sur-Saone. His father was a wealthy attorney and he had one sister and two brothers.
He studied at the Oratorian college in Angers. After teaching in college and serving the French army for some years he was discharged due to ill health.
In 1807 he and his brother Claude invented the first internal combustion engine, which was installed in a boat on the river Saone. They called it Pyredophore.
In 1816, after experimenting with varies substances, he invented the process of Heliography and produced the first known photograph with the camera obscura.
Although Niepce presented his discovery to the Royal Society in London, in 1827, he was never able to market his invention partly due to his persistence in keeping his method to himself.
Later on in 1829, he made partnership with the french artist and a camera obscura specialist - Louis Jacques Mande Daguerre.
They continued working and experimenting until his sudden death, without none of his inventions being officially acknowledged. Niepce died on the 5th July 1833.
References:
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013.Nicephore Niepce. [online] Available at : <http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/414651/Nicephore-Niepce > [Accessed 31 October 2013].
Harry Ransom Center, (n.d).Joseph Nicephore Niepce. [online] Available at: < http://www.hrc.utexas.edu/exhibitions/permanent/firstphotograph/niepce/#top > [Accessed 31 October 2013].
Maison des Illustres,(n.d). Biography.[online] Available at : < http://www.niepce.com/pagus/pagus-bio.html > [Accessed 31 October 2013].
Gustav Le Gray
Gustav Le Gray was born on the 30th August 1820 in the outskirts of Paris. He took painting lessons with artist Paul Delaroche.
He married in 1844 and had two children.
Later in 1847 he began experimenting in the medium photography and produced his first daguerreotypes.
'Self portrait, Paris ',Spring 1848 - Daguerreotype
However, he was more interested in developing photographs on paper. In fact in his first treatises, which were published in 1850, he declared that 'the entire future of photography is on paper.'(The Metropolitan Museum of Art,2000-2013)
He invented the waxed-paper negative process which made prints more sharper. It could be prepared beforehand and even 'developed days after the photograph was taken.' (Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013)
He taught many known french photographers such as Charles Negre, Henri Le Secq, Olympe Aguado, Nadar, his brother Adrien Tournachon and Maxime Du Camp.
In 1851 he was one of the first five chosen photographers by the Commission for Historic Monuments to make a photographic inventory of the ancient monuments in France.
Northern facade of the chateau de Chenonceau, 1851
He was also a founder member of the Societe Heliographique.
In 1855, he opened a portrait studio at the Boulevard de Capucines in Paris, which later became the studio of Nadar.
His most famous work is that of the views of Fontainebleau Forest and seascapes, where he combined two negatives - one for the sky and another for the sea with different exposures.
'The Brig', 1856
Le Gray had to dissolve his company due to huge debts. In 1860 he closed his studio and boarded a yacht belonging to the writer Alexandre Dumas, abandoning his family and escaping his creditors.
After two months, due to a conflict with Dumas, he was abandoned in Malta.
Later he travelled to Lebanon and then to Egypt. While still photographing he became a professor of drawing and painting at the Ecole Polytechnique of the viceroy in Cairo.
He died in Cairo in 1884.
References:
The Metropolitan Museum of Art,2000-2013.Gustave Le Gray(1820-1884).[online] Available at : < http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/gray/hd_gray.htm> [Accessed 3 November 2013].
J.Paul Getty Trust,(n.d).Artists.[online] Available at : <http://www.getty.edu/art/gettyguide/artMakerDetails?maker=1913> [ Accessed 3 November 2013].
The Museum of Modern Art,2013.Gustave Le Gray (French 1820-1882). [online] Available at : < http://www.moma.org/collection/artist.php?artist_id=3429 > [Accessed 3 November 2013].
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013. Gustave Le Gray. [online] Available at : < http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/242621/Gustave-Le-Gray > [Accessed 3 November 2013].
Colour Wheel
Colour wheel is a spectrum circle displaying how colours interact with each other. It is made up of 3 primary colours ( red, yellow and blue), 3 secondary colours which are created by mixing primary colours together (ex. red+blue= purple), and tertiary colours which are developed by mixing primary and secondary colours together.
Colours opposite each other in the colour wheel (ex. green and red) are called Complimentary as they balance each other.
Those next to each other 'work harmoniously together.' They are called Analogous and are usually pleasing to the eye.
Hue , Intensity and Value ;
Hue is the pure colour before being mixed with black or white.
Intensity also termed as saturation, is the amount of colour. The higher the saturation, the less grey colour there is.
Value also called brightness, is the 'overall intensity to how light or dark a colour is. '
Tints can be created by mixing white to the colour.
Shade is when black is added to the particular colour.
Tone is a 'softer variation of the original colour' and is composed by adding grey.
References :
Sattout,Julia,(n.d).Portrait PaintingMy Way: Workshop4 :Colour Theory.[online] Available at: < http://juliasattout.com/portrait-paintings/colour-theory/ > [Accessed 19 October 2013].
Williams,Shirley,2008-2012. A Basic Colour Wheel....the first step to unlocking the mysteries of color.[online] Available at:< http://www.color-wheel-artist.com/basic-color-wheel.html> [ Accessed 19 October 2013].
Future Publishing Limited,(n.d).What is a Color Wheel: how to find the perfect shades and hues for your photos.[online] Available at: < http://www.digitalcameraworld.com/2013/04/23/what-is-a-color-wheel-how-to-find-the-perfect-match-for-your-photos/> [Accessed 19 October 2013].
Tiger Colour,2000-2012.Basic color schemes-Introduction to Color Theory.[online] Available at : <http://www.tigercolor.com/color-lab/color-theory/color-theory-intro.htm#warm_cool_colors>[Accessed 19 October 2013].
Sin Ayden,2011.All About Colours. [online] Available at: < http://aydensin.blogspot.com/2012/05/all-about-colours.html> [Accessed 19 October 2013].
Vident.com,2013,Hue,Value and Chroma.[online] Available at: < http://vident.com/products/shade-management/color-theory/understanding-color-overview/hue-value-and-chroma/> [Accessed 19 October 2013]
Yahoo Answers,(n.d).What are hue,intensity &value?.[online] Available at : < http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20081026200927AAiAK5V> [Accessed 19 October 2013].
Chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro is a popular technique used in art. It derived from two Italian words which means clear and obscured or light and dark. Chiaroscuro is the balance of light and dark using strong contrast to create a dramatic and powerful effect while giving the illusion of a three-dimension appearance.
The first use of Chiaroscuro technique was in ancient Greek, however became crucial in Northern Europe in the late 15th Century.
Leonardo da Vinci used it in such paintings like the unfinished painting of 'Adoration of the Magi'. Nonetheless this technique 'truly came to life in the paintings of Caravaggio, during the late 16th Century' where he created a dark background and a strong directional light on the subject. (EmptyEasel.com)
The Flagellation of Christ, Caravaggio 1607
Rembrandt a dutch painter , born at the beginning of the 17th Century, continued to develop this technique and achieved three effects which are 'dramatic intensity, rhythmic visual harmony and psychological depth'. (Netto, Jeffrey A)
Self Portrait, Rembrandt 1629
The method used in photography to create contrast between dark and light -chiaroscuro , is known as Rembrandt lighting. It can be achieved either in studio or with natural light at the golden hour.
Chiaroscuro is very powerful on three-dimensional objects such as animals, human body and also in landscapes as it gives it a sense of volume.
References:
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013.Chiaroscuro.[online] Available at : <http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/110261/chiaroscuro> [Accessed 25 November 2013].
EmptyEasel.com.2006-2013.Chiaroscuro in Painting: The Power of Light and Dark.[online] Available at : <http://emptyeasel.com/2007/07/20/chiaroscuro-in-painting-the-power-of-light-and-dark/> [Accessed 25 November 2013].
Netto,Jeffrey A,1999.Rembrandt and the Technique of Chiaroscuro.[online] Available at : < http://www.nettonet.org/Nettonet/101%20Painting/Studies/Chiroscuro.htm> [Accessed 25 November 2013].
Kuriositas,2010-2013.The Chiaroscuro and the Rembrandt Lighting.[online] Available at : <http://www.kuriositas.com/2011/08/chiaroscuro-and-rembrandt-lighting.html >[Accessed 25 November 2013].
Andre Adolphe Eugene Disderi
Andre Adolphe -Eugene Disderi was born on the 28th March 1819, in Paris France. He studied painting and was also a member for theater troupe.
In 1843 he married his wife Genevieve - Elisabeth.
He began his career as a daguerreotypist. In 1848 he moved with his family to the city of Brest where he opened his first phtographic studio.
In 1853 he opened the largest studio in Paris and a year later he patented famous photographic Carte-de-visite.
They were a small format , six by nine centimetres, albumen prints mounted on cards. With the multi-optic camera he could expose eight diverse photographs on one plate.
It was only in 1859 that the carte-de-visite became popular after Napoleon stopped to take his picture at Disderi 's studio.
Infact by 1861 it was believed that he was the richest photographer in Europe, where he opened more studios even in London.
The carte-de-visite was even 'affordable for the lower middle-class', yet it was still in demand by many celebrities. (Encyclopaedia Brittanica)
The fact that he managed to photograph royalty and many celebrities made the carte-de-visite collectable.
It remained fashionable 'until the late 1860s, when it was replaced by the larger cabinet card format.(J.Paul Getty Trust)
Trying other portrait formats without success and after several bankruptcies, Disderi died on the 4th October 1889 in Paris, penniless, blind and deaf.
References:
The American Museum of Photography, 1998-2004.A Brief History of the Carte De Visite.[online] Available at : < http://www.photographymuseum.com/histsw.htm > [Accessed 27 December 2013].
Photographic Art & Science Foundation,2013. Andre Adolphe- Eugene Disderi.[online] Available at : < http://www.iphf.org/hall-of-fame/andre-adolphe-eugene-disderi/ > [Accessed 27 December 2013].
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,2013.Andre - Adolphe - Eugene Disderi.[online] Available at : < http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/165519/Andre-Adolphe-Eugene-Disderi > [Accessed 27 December 2013].
J.Paul Getty Trust,(n.d).Andre Adolphe-Eugene Disderi.[online] Available at :< http://www.getty.edu/art/gettyguide/artMakerDetails?maker=2075 >[Accessed 27 December 2013].
Art Directory,(n.d).Adolphe -Eugene Disderi.[online] Available at : < http://www.art-directory.info/photography/adolphe-eugene-disderi-1819/ > [Accessed 27 December 2013].
Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard James Muggeridge was born on the 9th of April, 1830 at Kingston-upon-Thames, England.
In 1850 he immigrated to America where he began working as a bookseller in New York.
It was in 1855 that he showed interest in photography and also changed his surname to Muybridge.
During a business trip, in Texas he suffered serious head injuries in a stagecoach accident. After his recovery he got more into photography. He took numerous lanscapes photographs, especially of Yosemite Valley and sold many of them under another name 'Helios'.
Yosemite Valley
It all begins in 1872 when a former governor of California Leland Stanford asked him to photograph his horse trotting fast, in order to prove that the four hooves were all off the ground at some point.
Leland Stanford
Muybridge concluded and confirmed Stanford 's theory a year later after many attempts.
However Muybridge 's work was disrupted after he shot and killed his young wife 's lover. In 1875 he was acquitted by the jury for justifiable homicide.
He continued improving and producing images of human and animals 'that capture progressive movements within fractions of a second.' (National Museum of American History)
He experiments with a battery of 12 cameras and later on with 24 cameras.
Muybridge's Chronophotography. Museu del Cinema
In 1879 he invented a projection device called Zoopraxiscope which projected a series of images to a screen as moving pictures.
He gave a succession of lectures, projecting his photographs in motion with his Zoopraxiscope.
Zoopraxiscope
In 1900 Muybridge returned to England where he died on the 8th May 1904.
References:
A & E Television Networks,LLC,1996-2013.Eadweard Muybridge.biography.[online] Available at: < http://www.biography.com/people/eadweard-muybridge-9419513?page=1 > [Accessed 30 December 2013].
The Museum of Modern Art,2013.Eadweard J. Muybridge(American,born England 1830-1904).[online] Available at : < http://www.moma.org/collection/artist.php?artist_id=4192 >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
National Museum of American History,(n.d).Freeze Frame Eadweard Muybridge's Photography of Motion.[online] Available at :< http://americanhistory.si.edu/muybridge/ >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
Absolute Astronomy.com,2013.Eadweard Muybridge.[online] Available at: <http://www.absoluteastronomy.com/topics/Eadweard_Muybridge >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
Museu del Cinema,(n.d).Muybridge 's Chronophotography.[video online] Available at : <http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9cXM_sV_D8s video >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
George Eastman
The entrepreneur and inventor George Eastman was born on the 12th July,1854 in New York.
He was the youngest of three children. His father died when Eastman was 8 years old. At the age of fourteen he dropped school in order to support his widowed mother and older sisters, one of whom was wheelchair-bound.
He began working for insurance companies while studying accounting at home in order to get better salary. In 1874 he was employed 'as a junior clerk at the Rochester Savings Bank.' (Kodak.com)
At the age of 24 he planned to make a trip to Santo Domingo.At his colleague 's advice he bought the photographic equipment, to keep records of his trip, which was too heavy to carry.
He never made the trip, however he began to research how to simplify the process and make it acessible to the public.
In 1880 he invented the formula for dry plates, the machine coating and also initiate his own company.
In 1885, along with William Hall Walker they patented paper roll films.
He was also the one who came up with the word 'Kodak'.
In 1888 the first kodak roll film camera was launched.
The famous slogan "You press the button,we do the rest" helped making photography available to millions of people.
A year later he issued the transperent film.
The Kodak company introduced the the Brownie camera in 1900, which was sold for only one dollar.
Eastman was reowned for treating his employees very well, infact he initiated the 'concept of profit sharing'. (Biography.com)
Following in 1919, he donated one-third of his company to his employees.
He also contributed to many Institutes such as the University of Rochester.
After suffering progressive disability and severe diabities he took his own life on the 14th March 1932 at the age of 77.
References:
A & E Television Networks,LLC,1996-2013.George Eastman.biography.[online] Available at : <http://www.biography.com/people/george-eastman-9283428?page=2 >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
Encyclopaedia Brittanica,Inc,2013.George Eastman.[online] Available at : <http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/177435/George-Eastman >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
Kodak,2010.George Eastman.[online] Available at : <http://www.kodak.com/ek/US/en/Our_Company/History_of_Kodak/George_Eastman.htm> [Accessed 30 December 2013].
Public Broadcasting Service(PBS),1995-2013.Gallery.[images online] Available at :< http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/eastman/gallery/01.htm >[Accessed 30 December 2013].
The world would be a much better place if there will be more people like George Eastman. Besides being a great inventor, he was well known for his philanthropy work and how he treated his employees as his own family by even sharing the company profit with them.
Tintype
Tintype originally patented as the ferrotype is an image produced on a thin on a thin iron plate, instead of on paper or on glass.
Two young boys in a goat cart, c.1880
It developed from the ambrotype and was invented in 1856, by a professor of chemistry and physics - Prof. Hamilton L. Smith , in Ohio America.
The process involves thin sheet of iron covered with a layer of black paint. After, coating one side of the iron sheet with the wet collodion. It is exposed while collodion is still wet and processed immediately after.
Like ambrotype , collodion negative would show 'as a positive image when viewed against a dark surface'. It was also finished with a layer of varnish. (Edinburgh City Librarier and Information Services).
Since images are not processed from a negative, they would always be reversed.
Ferrotype portrait of a mother and baby, c.1875
Tintype became very popular from the 1860s,, particularly during the American Civil War. They were more durable than ambrotypes and could be mailed home without being destructed or shattered on the way.
It remained popular through the first decades of the twentieth century due to being very cheap and hence masses of people could afford it.
Tintype was frequently used by travelling and seaside photographers, and also in county fairs.
References:
International Center of Photography,2013. Past Exhibition.[online] Available at: < http://www.icp.org/museum/exhibitions/america-and-tintype >[Accessed 23 November 2013].
HeartlandScience,2005.Tintype Photography.[online] Available at: <http://www.heartlandscience.org/comm/pdf/tintype.pdf> [Accessed 23November 2013].
Edinburgh City Librarier and Information Services,(n.d).Tintype or Ferrotypes.[online] Available at: < http://www.edinphoto.org.uk/1_early/1_early_photography_-_processes_-_tintype.htm> [Accessed 23 November 2013].
National Media Museum,(n.d).How to spot a ferrotype, also known as tintype (1855-1940s). National Media Museum blog,[blog]. Available at : < http://nationalmediamuseumblog.wordpress.com/2013/05/25/find-out-when-a-photo-was-taken-identify-ferrotype-tintype/> [Accessed 23November 2013].
Man Ray
Born named Emmanuel Radnitzky, on the 27th August, 1890 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Man Ray grew up in New York, but spent the greater part of his life in Paris.
In 1903 he enrolled in high school and had lessons in freehand drawing and industrial architecture. He turned down the offer to study architecture. He started frequenting Ferrer Center, which functioned under libertarian principles, with classes in drawing, and visiting the "291" gallery of Alfred Stieglitz. In 1913 made the first cubist painting: Portrait of Alfred Stieglitz.
Stieglitz who was acknowledged as the pioneer in the improvement of Pictorial Photography, was born on the 1st
January, 1864 in Hoboken, New Jersey, U.S.
He was an art dealer, publisher, advocate for the Modernist movement in the arts.
He studied to become an engineer in Germany, but soon switched to photography and returned to New York in 1890.
He was known to appreciate women and married his first wife, Emmeline Obermeyer. Her father was affluent and generous with money, so Stieglitz didn't need to work for a while.
In 1905, along with he photographer and painter Edward Steichen, he established the Little Galleries of the Photo-Secession at 291 Fifth Avenue in New York. It was initially an place for exhibiting work by Photo-Secessionist photographers however it became more a center for the exhibition of modern European and American artists. He managed to improve photography 's status as a medium of fine art like painting and sculpture through the various exhibitions that he organized.
In 1910 the Albright Gallery of
Buffalo, New York, offered him its entire gallery space to do a photographic
exhibition.
In 1903 he enrolled in high school and had lessons in freehand drawing and industrial architecture. He turned down the offer to study architecture. He started frequenting Ferrer Center, which functioned under libertarian principles, with classes in drawing, and visiting the "291" gallery of Alfred Stieglitz. In 1913 made the first cubist painting: Portrait of Alfred Stieglitz.
Portrait of Alfred Stieglitz, 1913
Radnitsky married Adon Lacroix in 1914 and changed his family name to Man Ray. However it was a short marriage, as they separated in 1919.
In 1915 he published a book of diverse writings. He started photographic his paintings, and had his first exhibition in November, 1915.
The same year, Man Ray met French artist Marcel Duchamp, and together they collaborated on many inventions (including an anaglyphique film) and formed the New York group of Dada artists.
Man Ray and Marcel Duchamp, 1924
In 1921, Ray moved to Paris and became associated with the Parisian Dada and Surrealist circles of artists and writers.
His experiments with photography included rediscovering how to make "camera-less" pictures, which he called rayographs. After experimenting with a Cubist style of painting, he moved toward abstraction. In 1921 he made his first rayograph.
Rayograph The Kiss, 1922
In 1917 he started creating his first aerograph paints: Suicide and La Voliere.
Man Ray even collaborated with Tristan Tzara, designing his first chess set.
In 1922 he was doing many portraits including those of Gertrude Stein, Georges Braque, James Joyce, Jean Cocteau...and did cover photographs for the magazines Mecano, The Little Review, Ma, Les Feuilles Libres, and Aventura. He also was a fashion photographer for Paul Poiret. He also made his first movie The Return to Reason, which was eventually presented at the Theatre Michel.
Man Ray, Portrait of Gertrude Stein
Man Ray found love again with the model Adrienne Fidelin. He spent his summers in the South of France, at Mougins, with her and his collaborators, one of whom was Pablo Picasso. Ray and the latter made his movie together, then from 1938 he tried to devote himself solely to painting.
Model Adrienne Fidelin with her lover, the iconic photographer Man Ray in the 1930s.
Man Ray remarried in a double wedding in Beverly Hills: Man Ray to Juliet Browner and Max Ernst to Dorothea Tanning.
Juliet Browner,1945
Ray died in Paris, on the 18th November, 1976. His career was distinctive above all for the success he achieved in both the United States and Europe. Working on several media, Man Ray's art included paintings, sculptures, collages, aerographs, movies, constructed objects and photography.
References:
The Art Story Foundation,2014.Man Ray (born Emmanuel Radnitzky).[online] Available at: <http://www.theartstory.org/artist-ray-man.htm> [Accessed 17 January 2014].
A & TelevsionNetworks,LLC,1996-2013. Man Ray. [online] Available at: <http://www.biography.com/people/man-ray-9452778 >[Accessed 17 January 2014].
WikipaintingsVisual Art Encyclopedia,(n.d). Portrait of Alfred Stieglitz.[image online] Available at: <http://www.wikipaintings.org/en/man-ray/portrait-of-alfred-stieglitz-1913>[Accessed 17 January 2014].
The Museum of Modern Art,2014. The French Avant-Garde of the 1920s.[image online] Available at: < http://www.moma.org/explore/inside_out/2010/04/13/the-french-avant-garde-of-the-1920s> [Accessed 17 January 2014].
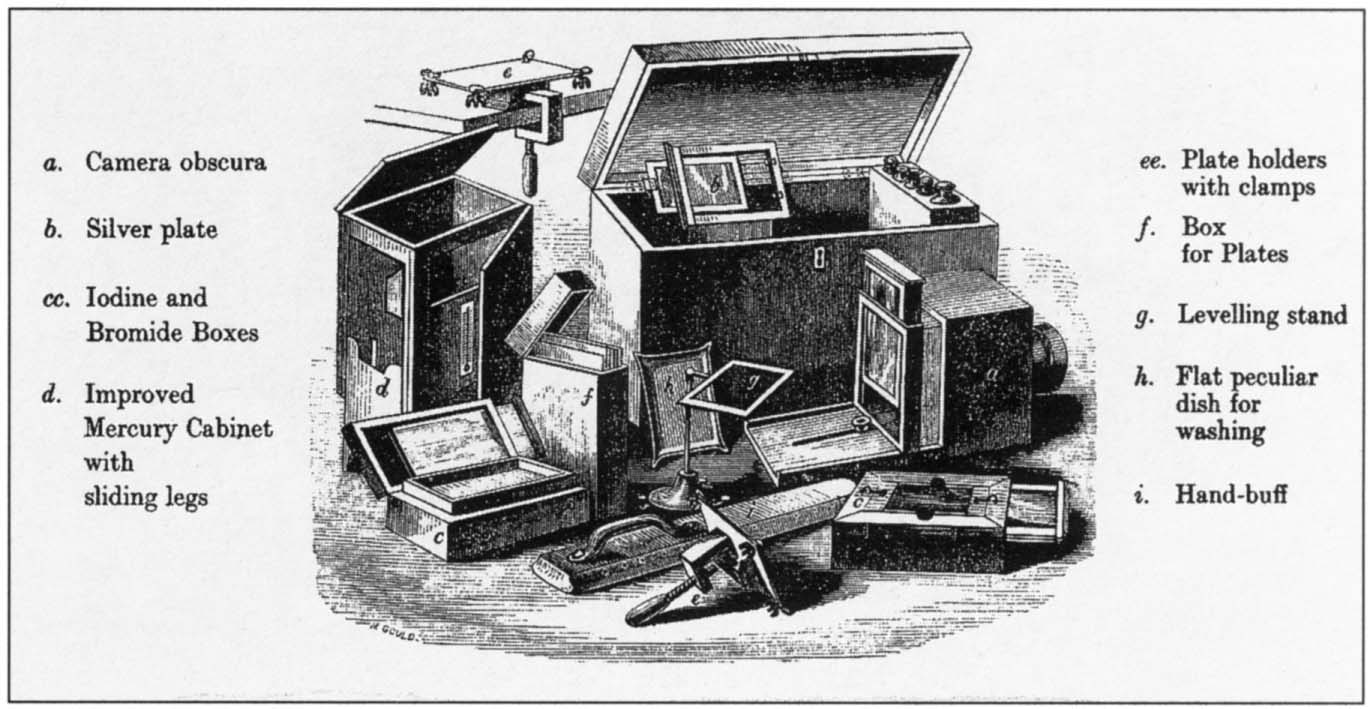
Daguerreotype
Daguerreotype is a photograph taken by an early method which consists of a positive image formed by an iodine-sensitized silvered plate and mercury vapour.
This was invented by the french inventor, and artist Louis-Jacques-Mande Daguerre. On the 7th January 1839, Louis Daguerre’s “daguerreotype” process was announced to the French Academy of Sciences by eminent astronomer and physicist François Arago. The publication of the process took place on the 19th August of the same year.
Portrait of Louis Daguerre (1787–1851)
The process involved polishing a sheet of copper with a metallic silver coating and then exposing it to iodine vapour, until it it covered evenly.
The plate can then be exposed in the camera in bright daylight.
Once photograph is taken it will be developed by exposing the plate to the vapour of mercury. The mercury will blend with the silver.
The remains of silver iodide is washed off and the image will be permanent.
One of the advantage of the daguerreotype is that details in a can be very clear and sharp. The image itself consists of higher or lower densities of microscopic silver and mercury particles.
L'Atelier de l'artiste, an 1837 daguerreotype by Daguerre
A daguerreotype studio was often situated at the very top of a building, which had a glass roof to let in as much light as possible. The subject to be photographed sat on a posing chair placed on a raised platform, which could be rotated to face the light. The sitter's head is held still by a clamp.
By the early 1860s the daguerreotypes was replaced by the wet collodion process.
References:
A & E Television Networks,LLC,1996-2013. Louis -Jacques- Mande Daguerre.[online] Available at: <http://www.biography.com/people/louis-jacques-mand%C3%A9-daguerre-40754>[Accessed 19 January 2014].
About.com,2014. Daguerreotype.[online] Available at :< http://inventors.about.com/od/dstartinventions/a/Daguerreotype.htm> [Accessed 19 January 2014].
Sussex Photohistory Website,2005. The Daguerreotype Process. [online] Available at : < http://www.photohistory-sussex.co.uk/dagprocess.htm> [ Accessed 19 January 2014].
Curious-eye.com,2009. L'Atelier de l' artist. [image online] Available at : < http://www.curious-eye.com/photography_pg4.php > [Accessed 19 January 2014].
Kraszna-Krausz,A.,1978, The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography,Desk Edition, London:Focal Press. [Accessed 19 January 2014].
Alfred Stieglitz
He was an art dealer, publisher, advocate for the Modernist movement in the arts.
He studied to become an engineer in Germany, but soon switched to photography and returned to New York in 1890.
He was known to appreciate women and married his first wife, Emmeline Obermeyer. Her father was affluent and generous with money, so Stieglitz didn't need to work for a while.
From 1893 to 1896,
Stieglitz was editor of American Amateur Photographer magazine; a journal of
the Camera Club of New York. This position allowed him to advance the
photographers and policies he favoured. However his editorial style proved to be rude, and by 1902 Stieglitz was forced to resign.
That same year Stieglitz founded
a new organization called the Photo-Secession, and produced the avant-garde photographic journal 'Camera Work'.
291 Fifth Avenue, New York City, avant 1913
In the period
of 1917 to 1925, he took around 300
photographs of Georgia O'Keeffe who became his wife in 1924, after Stieglitz
divorced his first wife.
Georgia O'Keeffe, photography by Alfred Stieglitz, 1918, platinum print.
Stieglitz also produced series of
images illustrating the changing skyline of New York, and also the ambience of
his summer home at Lake George in New York.
“Study at Lake George”
In the final decades of his life,
Stieglitz devoted his time chiefly to running his galleries and he made
photographs less frequently as he grew older.
He died on the 13th July, 1946 in New York City, New York at the age of 82.
References:
Victoria and Albert Museum,2014.Alfred Stieglitz.[online] Available at: <http://www.vam.ac.uk/content/articles/a/alfred-stieglitz-exhibition/ >[Accessed 25 January 2014].
J. Paul Getty Trust,(n.d). Alfred Stieglitz.[online] Available at : <http://www.getty.edu/art/gettyguide/artMakerDetails?maker=1851>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
The Metropolitan Museum of Art,2000-2013. Alfred Stieglitz (1864-1946) and His Circle.[online] Available at :< http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/stgl/hd_stgl.htm>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
Index of Modernist Little Magazines,2014.Camera Work Description.[online] Available at :<http://sites.davidson.edu/littlemagazines/camera-work-description/>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
Aleksandr Mikhailovich Rodchenko
Aleksander Mikhailovich Rodchenko was a Russian artist, sculptor, photographer and graphic designer. He was born on the 5th December 1891, in Saint Petersburg, Russia.
In 1905, Rodchenko moved to Kazan with his family.
During the period between 1908-1910 Rodchenko was a dental technician at Dental School of Dr. Natanson. Afterwards he enrolled in the Kazan School of Fine Arts in 1910 till 1914. He was a pupil of Vladimir Mayakovsky amongst several others. His work was initially influenced by Cubism, then became a supporter of Cubo-Futurism. His early paintings were influenced by his European surroundings, following the developments of Suprematism and Futurism. However he eventually turned his art to abstract art.
In 1915, nearly a year after World War I began in Russia, Rodchenko registered in the Graphic section of the Stroganov School of Applied Art.
During his time in Moscow, he was part of many exhibitions. He taught painting theory in the school-studio of Proletkult in Moscow.
He worked with a wide variety of media as a decorator, furniture and theatre designer, printer, painter, sculptor, and photographer.
From 1917 to 1921 Rodchenko had his own exhibition in Moscow, produced his first collages using found photography, and is a part of 16 art exhibitions. During this time his style was completely abstract and highly geometric aesthetic.
Non-Objective Painting: Black on Black
1918
1918
Untitled
1920
1920
In 1921 Rodchenko replaced Wassily Kandinsky as Chairman of State Institute of Artistic Culture (INKHUK) and Chairman of Museum Bureau and Russian State Art Acquisitions Commission in Russia. During the movement he formed the first working group of Constructivists.
He was married to the artist Varvara Stepanova.
Rodchenko and Stepanova
1920
1920
In 1923 he started creating his own photography and received many graphic design commissions for book covers and posters.
Poster for Trekhgornoe Beer
1923
1923
In 1925 Rodchenko won four silver medals at Paris International Exhibition. He was a part of over 50 art exhibitions.
In 1928 Stalinists attacked Rodchenko and his work and was implicated of supporting Trotsky and his ideas. His exhibitions were cancelled and was dismissed from major projects and jobs.
He ended up unemployed which lead to health problems and depression.
He lived in poverty and darkness till 1954, after the death of Stalin. Only then could he restart painting and worked on various literary projects with his wife.
He died of stroke on the 3rd December, 1956 in Moscow.
References :
A World History of Art,(n.d). Alexander Rodchenko.[images online] Available at : <http://www.all-art.org/art_20th_century/rodchenko1.html>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
ImDb.com,Inc.,1990-2014.Alexander Rodchenko.[online] Available at :<http://www.imdb.com/name/nm0734447/bio>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
Love to Know,Corp,1996-2014.Alexander Mikhailovich Rodchenko Facts.[online] Available at:<http://biography.yourdictionary.com/alexander-mikhailovich-rodchenko>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
Henri Cartier - Bresson
Henri Cartier-Bresson was born on the 22nd August, 1908 in Chanteloup, France .
Educated in Paris, Cartier-Bresson developed an early love for literature and the arts. He took his creativity genes from his artist great-grandfather and his uncle who was a famous printer. Even his father experimented in drawing.
Early in his adulthood he drifted toward communism but keep art as the main focus in his life. In 1927 he began a two-year stint studying painting under Cubist, André Lhote, then moved to Cambridge University to continue his art and literature courses. He was influenced by the visual aspects of Surrealism.
He took up photography after travelling to Africa in 1931 to hunt antelope and boar. He got quickly uninterested in hunting but stayed there for a while to capture life in Africa through photos.
Grand Lahou, Abidjan, Ivory Coast, 1930-31
He had his first exhibitions and publications by 1933. Visits to Mexico and the United States, and a job as an assistant to filmmaker Jean Renoir, in France for 3 years, helped develop his work, but it was World War II that launched his international career.
Cartier-Bresson is often labelled as "the father of photojournalism" for his photos of famous events and people from the 1930s to the 1970s.
Besides applying geometry to his images, he paid attention to detail and especially composition.
He only used 50mm lens and sometimes a 90mm lens.
Cartier-Bresson 's First Leica
In 1940 Cartier-Bresson joined the army but was imprisoned by the Germans. He escaped in 1943, after two unsuccessful attempts and worked with the Resistance.
In 1945, Cartier-Bresson captured the liberation of Paris and later in 1948 he documented Gandhi just before his death.
He is famous for his portraits of famous artists, thinkers and politicians, including Albert Camus, Truman Capote, Che Guevara and Marilyn Monroe.
Marilyn Monroe
He co-founded the photo department Magnum Photos in 1947, and was commissioned by the United States to direct a documentary about the return of French prisoners.
He published his first book, The Decisive Moment, in 1952.
In 1966, Cartier-Bresson quit Magnum, abandoned photography and returned to his first love - drawing and painting.
In 2003, Cartier-Bresson, along with his wife and daughter created the Foundation Henri Cartier-Bresson in Paris in an effort to preserve his work.
At a pronounced age of 95, Henri Cartier-Bresson passed away in Provence on the 3rd August, 2004.
References:
Pearson Education,2000-2014.Henri Cartier- Bresson.[online] Available at:<http://www.infoplease.com/biography/var/henricartierbresson.html>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
A & E Television Networks,LLC.,1996-2013.Henri Cartier -Bresson.[online] Available at :<http://www.biography.com/people/henri-cartier-bresson-9240139>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
Atget Photography.com,(n.d).Henri Cartier -Bresson, French,1908-2004.[online] Available at:<http://www.atgetphotography.com/The-Photographers/Cartier-Bresson.html>[Accessed 25 January 2014].
The Metropolitan Museum of Art,2000-2013.Henri Cartier-Bresson(1908-2004).[online] Available at :<http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/cabr/hd_cabr.htm>[Accessed 25 January 2014].


































































No comments:
Post a Comment